
We Protect Roofs to Last for 10-15 Years Longer.
Nano Coatings and Sealants for Concrete and Shingles
Explore the possibilities with Nanoguard
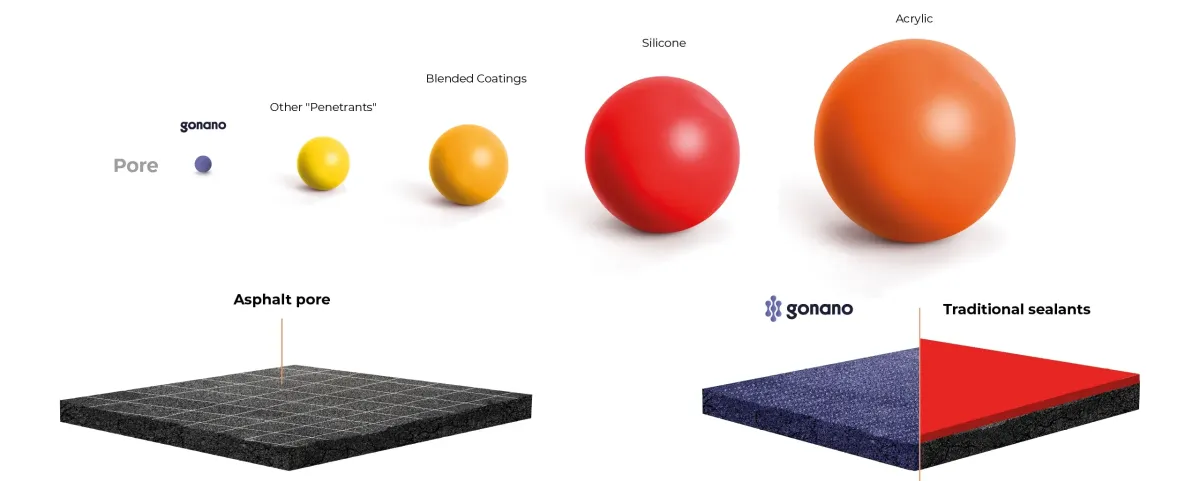
GoNano vs Traditional Sealants
GoNano’s asphalt enhancement sealant has been validated by the scientific community.
Traditional Sealants
Acts as an isolated, protective layer
Typical repair on microscale, adds layer of oil
Less durable, flexible and resilient to aging due to environmental conditions
NanoGuard sealant
Modifies the mechanical properties of asphalt
Nanoscale (1000X smaller than a micro meter) forms precise shapes into asphalt pores
Bonds to each asphalt shingle, and each shingle to the other

GoNano Advantages

Improved flexibility
Elastic strain resilience, high tensile strength to pressure and load, fracture aversion.

Hydrophobic
Impervious to moisture infiltration.

Adaptable fatigue life
Endures greater cycles and seasons of stress.

GONANO ADVANTAGES
The result: research shows one treatment of GoNano extends the average roof’s lifespan by 10 to 15 years.
Once modified, the new structural form of the asphalt enhances its durability, specifically its flexibility, hydrophoby, and anti-aging performance.
Permanent Structure Modification
The GoNano Effect
01
Modifies the molecular structure of asphalt shingles.
02
After application, reaction occurs with each shingle.
03
During reaction, both organic and inorganic material create new chemical links, called S1 particles.
02
S1 particles enter into asphalt pores and move outward, connecting with other shingles.
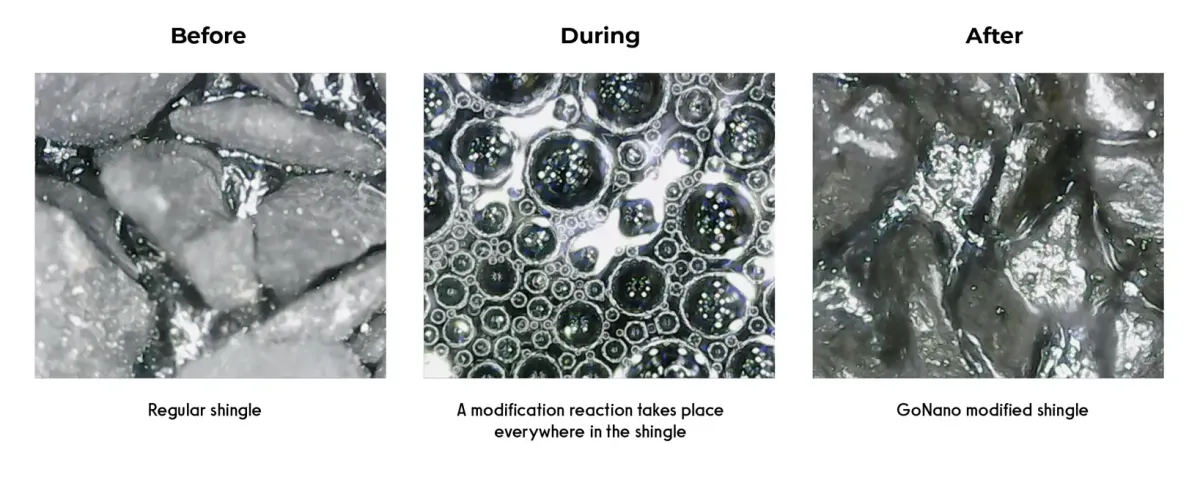
The result: a unified barrier against strains caused by environmental factors
The evolution of GoNano technology created a shift in how sealants are approached. A regular shingle is sealed with oil, filling up the space in between shingles. GoNano modifies the molecular structure of asphalt shingles permanently. After application, a reaction occurs within each shingle. This reaction fuses both organic and inorganic material, creating new chemical links, called S1 particles. These S1 particles link shingle granules together, working from the inside out, creating a unified barrier against environmental strains and saves you money by extending the lifespan of your roof.
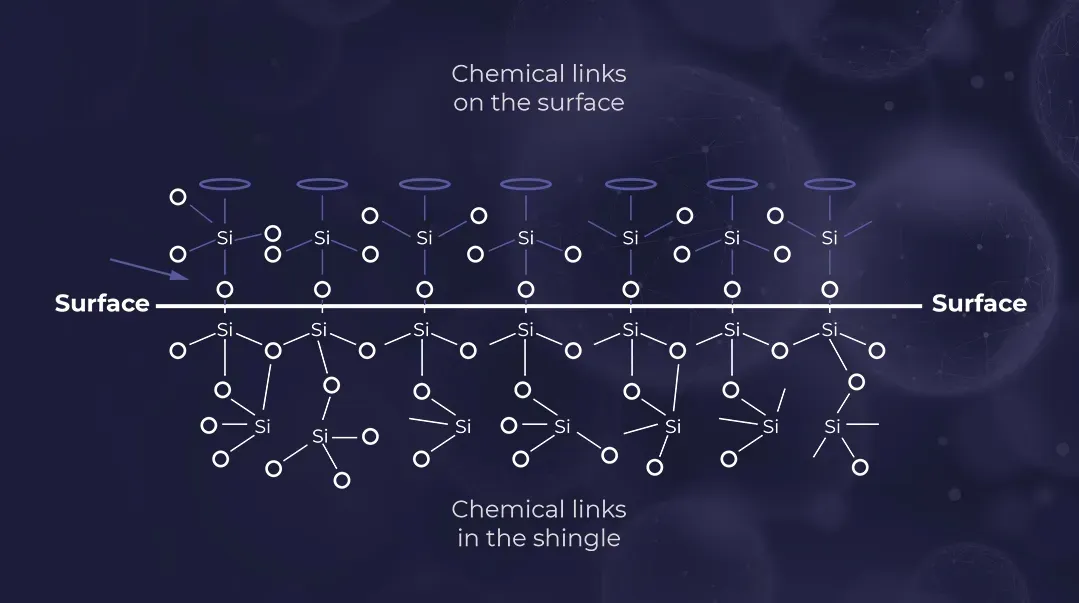

Advantages of Molecular Structure Modification
• Increased resistance to hail storms and high winds
• Cleans and prevents the growth of algae
• Prevention and reduction of walter infiltration
• Preserving and regenerating shingle color
• Maintaining granule composition
• Effective evacuation of ice and snow
Nanosilica

Material
Similar to silica, an inorganic nanomaterial, composed of high silica density.

Manufactured
Synthetically created by precipitation, hydrothermal/solvothermal, or thermal reduction processes

Performance
Modification occurs from pozzolanic reactivity (pore-filling).
Nanosilica is an inorganic nanomaterial, similar to silica, but it is characterized by high silica density (99%). It must be synthetically created through one of three processes: the precipitation pathway (silica reacts in a solvent through purification and dispersion), the hydrothermal/solvothermal pathway (silica goes through precipitation, high pressure and temperature conditions), or thermal reduction (silica is placed in temperatures of up to 1700°C to 2300°C). Once nanosilica is formed, its improved performance is attributed to its pozzolanic reactivity (the chemical reaction that occurs for pore-filing).
GONANO CLASSES
Roof Classes and Certification
CLASS 1
Least resistant, can withstand at most a 1.25-inch steel ball test.
CLASS 2
Can withstand at most a 1.5-inch steel ball test.
CLASS 3
Can withstand at most a 1.75-inch steel ball test.
CLASS 4
Highest resistance, can withstand up to a 2-inch steel ball test.
Classifications for shingled roofs are put through a standardized process by Underwriters Laboratories to determine a roof’s impact resistance to falling objects, emulating a hailstorm. There are four categories: Classes 1, 2, 3 and 4, in order of least resistant to most resistant. In order for GoNano to earn a Class 4 certification, a 50.88mm(2-in) diameter steel ball was dropped from 20 feet above a vulnerable section of a shingled roof. Following these tests, roofs showed no signs of damage and/or cracking. A Class 3 steel ball is smaller by a quarter of an inch in diameter, and so on for Classes 2 and 1. Class 4 is shown to have the highest impact resistance, a low loss of granules and a lifespan of 22 to 25 years. The less effective Class 1 has little-to-no impact resistance with a higher loss of granules and decade-shorter lifespan. One treatment from GoNano’s sealant transforms Class 1 shingles into Class 3, and two treatments into Class 44.
Environment
In the coming years, the effects of climate change will mean an increase in severity of hail storms. Impact-resistant shingles will be a necessity for protection against increased frequency and strength of future storms.
GoNano’s technology provides a major innovation that transforms traditional roofs into hailstorm resistant roofs at a fraction of the cost of hailstorm resistant shingles.
We are the first and only company to offer this technology to the residential and commercial market.
GoNano has been tested to comply with the highest North American standards.
In addition, GoNano’s technology is completely safe for the environment and poses no threat to human health.
The Occupational Safety and Health Administration categorized GoNano’s technology as “quickly biodegradable”, “no bioaccumulation potential”, and “no harm to aquatic organisms”.
Classifications for shingled roofs are put through a standardized process by Underwriters Laboratories to determine a roof’s impact resistance to falling objects, emulating a hailstorm. There are four categories: Classes 1, 2, 3 and 4, in order of least resistant to most resistant. In order for GoNano to earn a Class 4 certification, a 50.88mm(2-in) diameter steel ball was dropped from 20 feet above a vulnerable section of a shingled roof. Following these tests, roofs showed no signs of damage and/or cracking. A Class 3 steel ball is smaller by a quarter of an inch in diameter, and so on for Classes 2 and 1. Class 4 is shown to have the highest impact resistance, a low loss of granules and a lifespan of 22 to 25 years. The less effective Class 1 has little-to-no impact resistance with a higher loss of granules and decade-shorter lifespan. One treatment from GoNano’s sealant transforms Class 1 shingles into Class 3, and two treatments into Class 44.